Written by Merche Martínez
Index
One of the most common indexability problems when I perform an SEO audit of a website is duplicate content. The purpose of this article is to define a guide with some points to review that we have detected in Human Level thanks to the experience gained after many years doing SEO consulting.
What is duplicate content?
Search engines index each content with a unique identifier which is the URL of the page.
It is essential that there is a one-to-one correspondence between a content and a URL.
Submitting the same content under two different URLs can be detected as duplicate content by search engines that consider duplicate content as an attempt to grab more positions on the results page. Therefore, they select one URL (usually the oldest or most popular) as the “original” source of the content and rank it higher, while others presenting the same content are relegated to the bottom. An example would be:
www.example.com/prueba
www.example.com/prueba-2 -> Same content
Revision of Google search results
Duplicate content detected by Google
An important indicator is provided by Google in its search results. To do this we must enter the command “site:” followed by the URL of the domain, like this: site:www.example.com. This search shows us all the indexed pages of the entered domain, and what interests us in this regard is on the last page. One trick to get to the last page of Google search results is the following. In the URL we can see the start parameter, if we are on page 2 the value is 10, if we are on the third page it is 20 and so on. Entering the value 990 takes us to the last page. It would look like this, start=990.
In case of duplicate content, the following message appears indicating that there are 490 pages that have not been shown in the search results because they are considered by Google as “very similar to those already shown”.
If we click on the link to repeat the search including the results that are not shown we will be able to see those pages that are considered duplicate content. Unfortunately they are not marked with an eye-catching background or anything that makes them stand out, I wish. So here we come to the point of reviewing the search results.
Duplicate content detected by review
Duplicate content can also be detected by reviewing the different pages of the search results by looking at the titles and snippets.
The title is one of the most important elements for calculating the on-page relevance of a page. If we look at the results, it is possible that several of the same titles will catch our attention. This may be an indicator of duplicate content.
If we detect several of the same titles we can check it with the command:
site:www.example.com intitle:title text
The same applies to the snippet, which is the text fragment that briefly describes the content of the page in the search engine results pages (SERPs). By default, this text usually matches the content of the page’s description meta tag. This point is very important because if we see repeated snippets it is very likely that we are dealing with duplicate content.
List of products “No results exist”.
Browsing the website we can detect listing pages that have no results. If these pages display a “No results” message, what we do is to enter the command in Google:
site:www.example.com “No results exist”
And we will see the indexed pages of the listings with no results. If the pages do not have content that differentiates them, they may be considered duplicate content.
Tools to detect duplicate content
Google Search Console
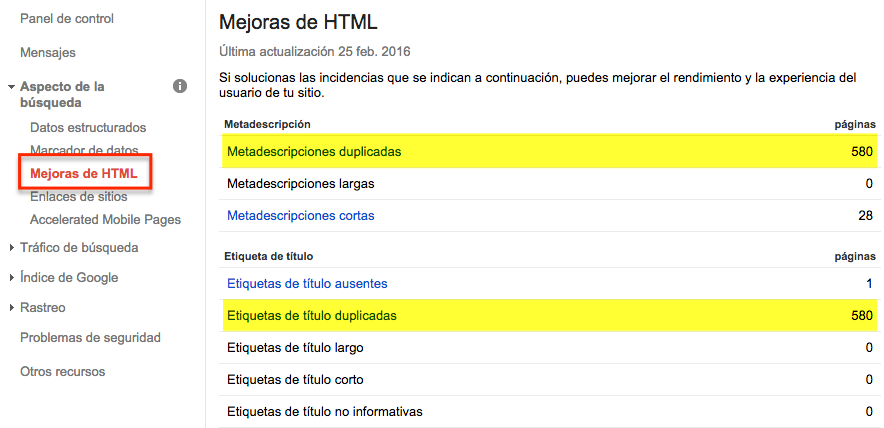
In Google Search Console we have the option of HTML improvements. In this section we see the titles and meta descriptions that Google has detected as duplicates.
If we click on duplicate title tags we see the pages with duplicate title tags and if we drop down the title we see in which pages that title is included. The same applies to the duplicate meta descriptions option.
Screaming Frog
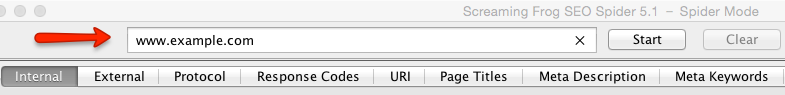
The Screaming Frog tool is a very useful SEO resource that among many other features has the option to show duplicate content. Screaming Frog is a paid tool, but it has a free version that allows you to crawl up to 500 URLs of a domain. In this free version we have available the option to view duplicate content, which is what we are interested in.
First we must capture the existing URLs on the site. To do this we enter the domain of our website.
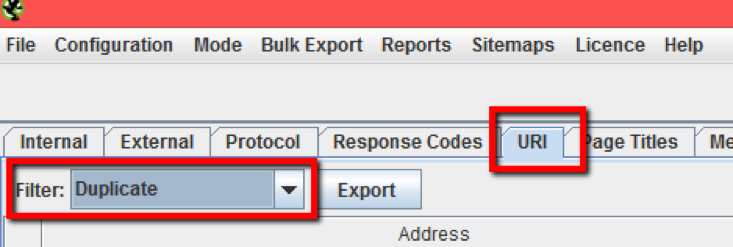
Once the crawl is finished, in the URI tab we select the duplicate filter and when we do so we see a list of pages with different URLs and duplicate elements such as title, meta description, H1, etc.
Mirror domains
Duplicate content can also occur between domains, when the content is exactly the same, they are called mirror domains. The most common case of mirror domains is between the main domain (example.com) and the subdomain www.example.com. With the command site:example.com -www you will see the indexed pages of the subdomains, if any.
We have also encountered published and indexed development environments that generate duplicate content. These environments can be on subdomains such as dev.example.com, pre.example.com or they can also be on a completely different domain.
Paginator
Paginators are cannon fodder for duplicate content. Some cases that we can find duplicate content in pagers are the following:
- First page: it is possible for the content of the first page to be displayed with and without the page=1 parameter.
www.example.com/listado
www.example.com/listado?pagina=1
- Last page: I have detected cases where the value of the paging parameter for the last page is not correctly controlled and the same result is returned for any higher value.
www.example.com/listado?pagina=4 -> Last page
www.example.com/listado?pagina=10
www.example.com/listado?pagina=100
With respect to the listing pages we have detected a common error and that is that they usually have the same title and meta description. We can easily detect this in the search results review and in the HTML enhancements section of Google Search Console.
It is possible that we can reach the same content from different navigation paths. It is logical that the product, service or listing cards of a website can belong to different categories. Let me give you an example to understand this case: to rent an apartment in Alicante we could follow the following navigation routes:
www.example.com ->
www.example.com/alquilar/ ->
www.example.com/alquilar/alicante/
or
www.example.com ->
www.example.com/alicante/ ->
www.example.com/alicante/alquilar/
In this case the pages www.example.com/alquilar/alicante/ and www.example.com/alicante/alquilar/ would return the same content and would be duplicate content.
Parameter index
We have seen this point specifically when I talked about pagers. But it can occur with any parameter.
It is possible that for a URL with parameters we find that for any value we put in the parameter we get the same result. For example, to sort a list there are the options order=ascending and order=descending, but if it is not well programmed, it may happen that for the value order=blablablabla it returns the same result as for any of the previous options. In that case it would be duplicate content.
Duplicate home page content
The content of the home page can easily be displayed in different URLs. Here are some examples that we usually find:
www.example.com
www.example.com/home.php
www.example.com/index.html
These pages can be linked from the main menu (home, home, etc.), from the logo link, from the footer or from any page. And yes, you guessed it, it would also be duplicate content.
Tags
A bad use of tags can generate pages with the same content. For example in blogs, I have found that it is common to create new tags for each article and these tags may not be reassigned to other articles. Each of these tags generates a listing page with a single item. These pages may be considered duplicate content.
External links
For several of the cases I have mentioned, such as order=blablablabla, you may think, but how is that URL going to be indexed if there is no link from my website to it? Very simple, you can be linked simply by mistake from another website and if that URL returns a 200 OK server code the page will be indexed.
Recommendations to avoid duplicate content
So what do I do if I have duplicate content? Sorry, there is no single formula, but here are some possible solutions:
- Canonical: for some cases the recommendation is to include the canonical link element correctly. In this way we can suggest to Google the page we want to be indexed. Here you will see some cases in which it is advisable to use the canonical link element.
- 301 redirect: for some cases it is advisable to perform a permanent 301 redirect from a URL with duplicate content to the URL that we consider correct for that content.
- 404 server code: in some cases it is possible that the page with duplicate content should not exist. In that case it should return a 404 server code.
As you have seen, duplicate content is a very common error in websites that you can detect in a relatively simple way and solve with the recommendations I have given you. Now that you have read the article I invite you to review your website and check that duplicate content is not a problem for you.