Written by Anastasia Kurmakaeva
Index
Toxic links are referral links received by our website, which negatively affect the authority and popularity of our website due to the low quality of links and the use of linkbuilding practices. This can include over-optimization of anchor texts with keywords, backlinks from websites not related to the subject matter of our content, among others.
Nowadays the inbound links or backlinks that a website has cannot and should not be taken lightly. Linkbuilding strategies and maintaining the right referral link profile to benefit us is becoming more and more complicated. This is partly because the practices that were used years ago, and are still used to some extent today, are not always natural and honest. To counteract them, search engines have imposed certain regulations to be followed, and have designed measures in the form of warnings and penalties that apply to websites that do not comply with them.
Types of penalties for toxic or unnatural links

Google Penguin and its predecessor, Google Jagger.
Google Jagger was the first Google algorithm update that began to devalue poor quality backlinks, such as those that came from link farms, or were reciprocal, purchased, etc.
But it was Google Penguin, launched back in 2012, that put an end to the practice of getting a disproportionate amount of spammy links. in order to manipulate the popularity and authority of a website, directly penalizing those portals that used malicious and low quality links in order to get a good boost in the rankings. rankings and occupy the top positions without really deserving it.
Yandex Minusinsk
The Russian search engine, for example, also launched an algorithm update in 2015 to combat backlinks of poor quality, forcing websites to clean up their popularity profiles under the threat of a penalty by the rankingsand even affect large companies, such as e-commerce and small websites on an equal footing.
But, wait. Why is website popularity so important?
A person who is outside of the SEO and online marketing world probably doesn’t quite understand the reason for all this “drama” around inbound links, which is totally understandable. But if we look at it in simpler and more generic terms, getting a quality referral link is getting a recommendation from that website, which considers you a reliable and respectable source, regarding your content, or the product or service you offer. If the website that has given us the link has good authority on the Internet, and is well respected by its visitors and readers, we will be gaining visitors who otherwise would most likely not know about us. If we add to this the added bonus of the vote of confidence that quality referral links give us, we are also talking about the increase in conversions and the possibility of getting more links on other websites or social networks. All this ultimately contributes to improve our positioning in search results, as it is a very important factor that is taken into account when calculating the relevance of a website.
Getting a quality referral link is getting a recommendation from a website.
If we manipulate our popularity with artificial links, worrying more about the quantity than the quality of them, or receive unwanted links from websites that in the eyes of Google – or any other search engine – are malicious, we could face a penalty that would make us losing positions in the results and, therefore, visibility in the search engines.
At Human Level we have dealt with several cases, both penalties and websites that were at risk of receiving at least a warning due to the large number of toxic links they were receiving, so we have extensive experience in this field.
Now, to the point.
What do we need to detect and remove toxic links?
To start purging our popularity profile and freeing it from toxic links, we need:
- A good list of all the links that our website receives, or at least, a sufficiently large sample if the portal is very large. We can obtain it by means of specialized tools that we will see next.
- Time, quite a long time. And patience.
- Be registered in Google Search Console to be able to use also Google Disavow Tool.
1. Tools to perform the audit
There are a lot of very complete tools that can help us in this complex and challenging task, such as SEMRush, Majestic, Moz’s Open Site Explorer, Cognitive SEO, Ahrefs, and of course, Google Search Console, among many others. They usually offer quite complete lists that we can download and pour into an Excel document, for a more thorough analysis; or we can go through them without leaving the tool’s website.
Where do you see or where can we find these listings?
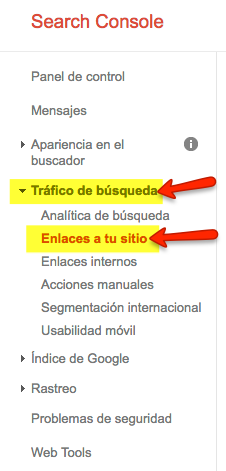
In Google Search Console:
Accessing the property we are interested in and clicking on “Search Traffic”, followed by “Links to your site”:
Their complete listing can be downloaded by clicking on “Download more sample links”.
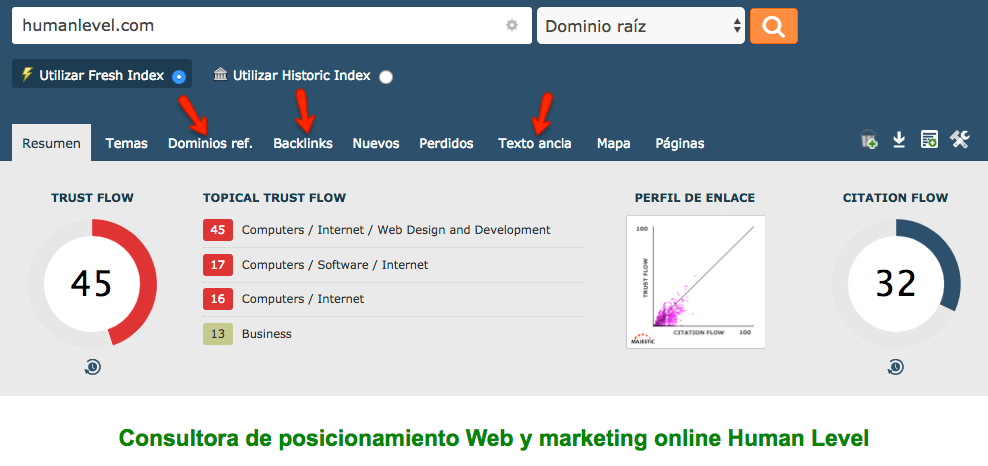
At Majestic:
In Majestic, being a tool completely focused on the inbound links that a site receives, there is no need to search for the section that analyzes them. We only have to enter the domain of the web site we want to audit in the search box, and we will obtain all the data we are interested in distributed by tabs:
In addition, with Majestic we can see at the moment the level of reliability of a domain, to which sector it belongs, and other information of interest.
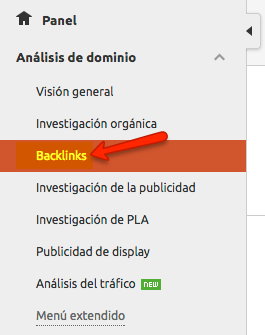
In SEMRush:
SEMRush also has a very complete backlinks section. In the same way, enter the domain name in the search bar and then click on the corresponding section.
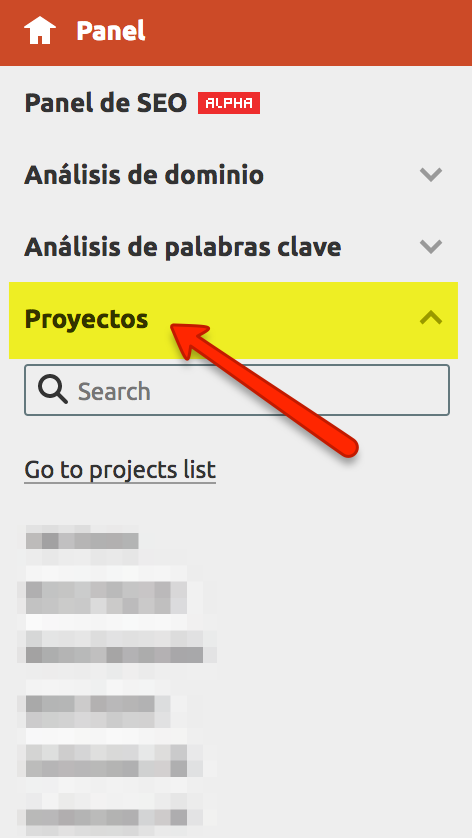
In SEMRush, we also have an additional way to monitor the referral links to our website, by creating a specific project for a certain domain:
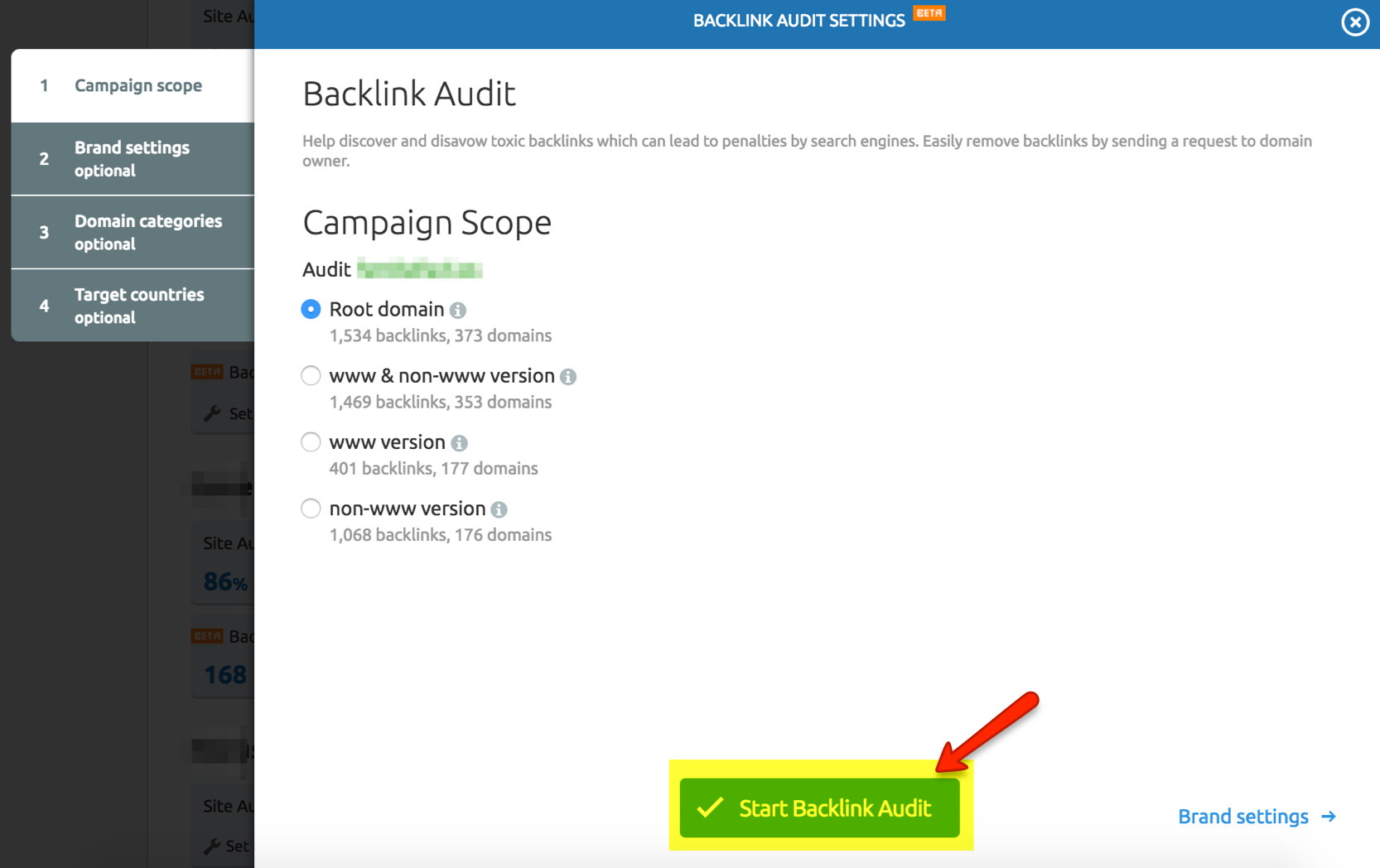
Once created (it is as easy as clicking on the “Add new project” button and entering the domain and project name), we can install the “Backlink Audit” module. During the installation, the tool will ask us to fill in some data, such as the scope of the analysis – at domain, subdomain, etc. level – as well as other optional information, such as:
- Brand details.
- Categories to which the website belongs (e.g. culture, science, business…)
- The target countries we are focused on.
Once the module is configured, it will provide constant monitoring of the site and will notify us when it finds a link that it considers suspicious.
As far as possible, it is best to be able to contrast the data from several tools, so that if one of them offers only a sample, we can complete it with the data obtained from another one.
2. Link Deduplication
Once we have obtained the lists from the different tools, it is important to carry out a previous analysis and cleaning of duplicate links in order not to do work in vain twice (or more).
This phase is essential, since when mixing data from different sources it is very likely that we will find a considerable amount of repeated links, and unless we have an exceptional -or rather supernatural- memory, we will end up reviewing the same links repeatedly, investing our valuable time in something totally unnecessary and easily avoidable.
3. Indicators we can look for to detect toxic links
We are not going to deceive you, detecting toxic links at first sight is not always easy. Some are really obvious, but others camouflage themselves beautifully. However, there are some patterns that we can look at in order to do it carefully, both for the context in which the link is found, its characteristics, or the characteristics of the domain or website that grants it. For example:
- Links with anchor text over-optimized with keywords from content totally irrelevant to the target page. Without further ado. If the content has zero relation to the target page, and the anchor text of the link is the target keyword, we are dealing with a link that is not going to do us any good. A crude example of this would be: we have an online socks store, but a link with the anchor text “socks” to our e-commerce appears on a website that has a page about a psychological disorder. This kind of thing should instantly set off alarm bells.
- Links with anchor text totally irrelevant to the landing page and to the content of the site from which they link. For example, if we have a portal that offers information about tourism in certain cities in Spain and we link to a website (probably of low quality) of job offers with the anchor text “labor contract”. It makes no sense and is a link that we are not interested in maintaining.
- Links with anchor text such as “sex”, “viagra” and similar. They usually come from portals identified as spam sites, so they are a clear example of links that we must get rid of at the root by disavowing them.
- Websites with a “dubious” or outdated appearance. This section includes websites that seem to have been left behind in time, in the 00’s or even the 90’s, and that include a lot of links; as well as those that are simply empty pages, that do not have any type of layout and its only content is a never-ending list of links with anchor text strange, over-optimized with keywords, or that do not represent in any way the linked pages of our website.
- Websites with suspicious domain names. Especially when they are several different domains but very similar to each other because they follow the same pattern (or even share DNS), and also link us from all of them. If we accompany it with their content or lack thereof and other factors such as the anchor text cause us doubts, we can at least put them on our “check back later” list. Perhaps later in the audit, and after having seen more examples of malicious sites, we will be able to classify them better.
- Web sites such as list-of-domains.xxx, domain-history.xxx and similar. Although technically they usually grant “nofollow” links, it will not be superfluous to include them in the disavow file just in case. They can have different extensions, but typically they are.org,.info,.net,.biz, etc., and they are not usually of the.com or ccTLD type (although we have come across cases that did have those extensions as well, so don’t rule them out).
- Inappropriate, pornographic or violent websites. They are not going to be positive for our website in any context.
- Websites from other countries, in other languages and with suspicious appearance. We may be linked to from malicious or irrelevant sites in other countries. If our strategy is focused on specific locations – either nationally or internationally – and we are linked to countries that are not part of our target market, it is likely that we are not interested in keeping the links they give us.
- Links in forum comments. These types of links usually include the term “thread” in the URL, which is the quickest way to identify them.
These are the main indicators, but there are many more aspects that we can look at and that are identified once an audit begins to be carried out.
4. Create disavow.txt file to upload to Google Disavow Tool
Once we have identified all the malicious links and those that we cannot get rid of in any other way than through their direct disavowal, we will make a list of all the domains and subdomains that provide them and we will add them to an disavow.txt file following the format below:
domain:ganardinero.biz domain:list-of-websites.info domain:holacocacola.org domain:getcashnow.net domain:ventadegatos.info domain:etcetc.tk
We will save it and upload it to the corresponding property in the tool.
Tools such as SEMRush or Cognitive SEO can generate this list automatically, as we mark the sites we consider malicious. Once the selection process is finished, we will download the file, check that we have not missed any website whose links we are interested in keeping, and we will upload it in the same way.
5. Other ways to debug inbound links
Another somewhat more tedious way to get rid of links that we do not want to convey their popularity is to write directly to the owners of the web sites that provide them and ask for their removal. In addition to taking even more time to find out how to contact them and write to them personally, in many cases it is likely that we will not get any kind of response.
However, when it comes to links that if approached differently (with a different or less optimized anchor text, for example) could benefit us, it is definitely worth taking the time to request their modification in writing to the owners.
The more refined our inbound link profile is, the less likely it is that we will be penalized by search engines, and it is also very likely that this will help us to achieve better positions in search results. For these and other reasons that we have seen in the article it is essential to devote our attention to this aspect of SEO optimization, and track the inbound links we receive with an appropriate frequency.