Written by Juan Antonio Castillejos
Index
All companies need to reach their audience, connect with them according to their nature or values, and, above all, make them aware of their products or services. In addition, we must convince them that our offer is the best option compared to the competition. To this end, it is essential to optimize the communication of content so that it is effective.
There is a fundamental figure that, once analyzed and defined, will help align the company’s communication with the needs of its public. This is the figure of the buyer persona.
If the company plans its communication strategy around the needs of the buyer persona and adopts its offer, content and tone to this, it will be communicating properly and it will be easier to convert users into customers.
What is a buyer persona?
A buyer persona is a fictitious figure in which companies project the characteristics that their potential customer would have, on different levels. The objective is to know this ideal customer in as much detail as possible and to adjust business communication to this profile. This information is obtained through various means, such as focus groups, surveys or market studies.
This process allows the company and its marketing teams to “humanize” the image of its target consumer, in order to define with greater detail and precision its communication or marketing campaigns. By knowing which user they are targeting and what circumstances surround them, companies can correctly target their communication, content and marketing campaigns.
Defining the buyer persona is key for the business
As we can see, correctly profiling the ideal user interested in our offer is key to the communicative success of the company, as it will allow:
- Knowing their needs: this study will allow us to know what this user profile expects from a product or service. In this way, the company will be able to improve its value proposition and communicate it more effectively.
- To know what doubts or points of friction they have regarding the product or service and what questions they must find answers to in order to acquire it. This will allow you to generate content so that, without leaving the website or landing page, the user can solve those doubts. We will also know their buying motivations and we will be able to use them as a sales argument.
- Generate messages in the right channels and with a language that fits their way of communicating. Depending on the user profile, the company will be able to generate content in the most appropriate channel for the user, depending on the objective.
In this way it will be possible to attract users at different stages of the conversion funnel and keep them identified or aligned with the brand as they move forward in their purchase decision.
How to know who your buyer persona is: obtaining data to build their profile
In order to compose an accurate buyer persona profile, we need reliable data and information that can be obtained in different ways:
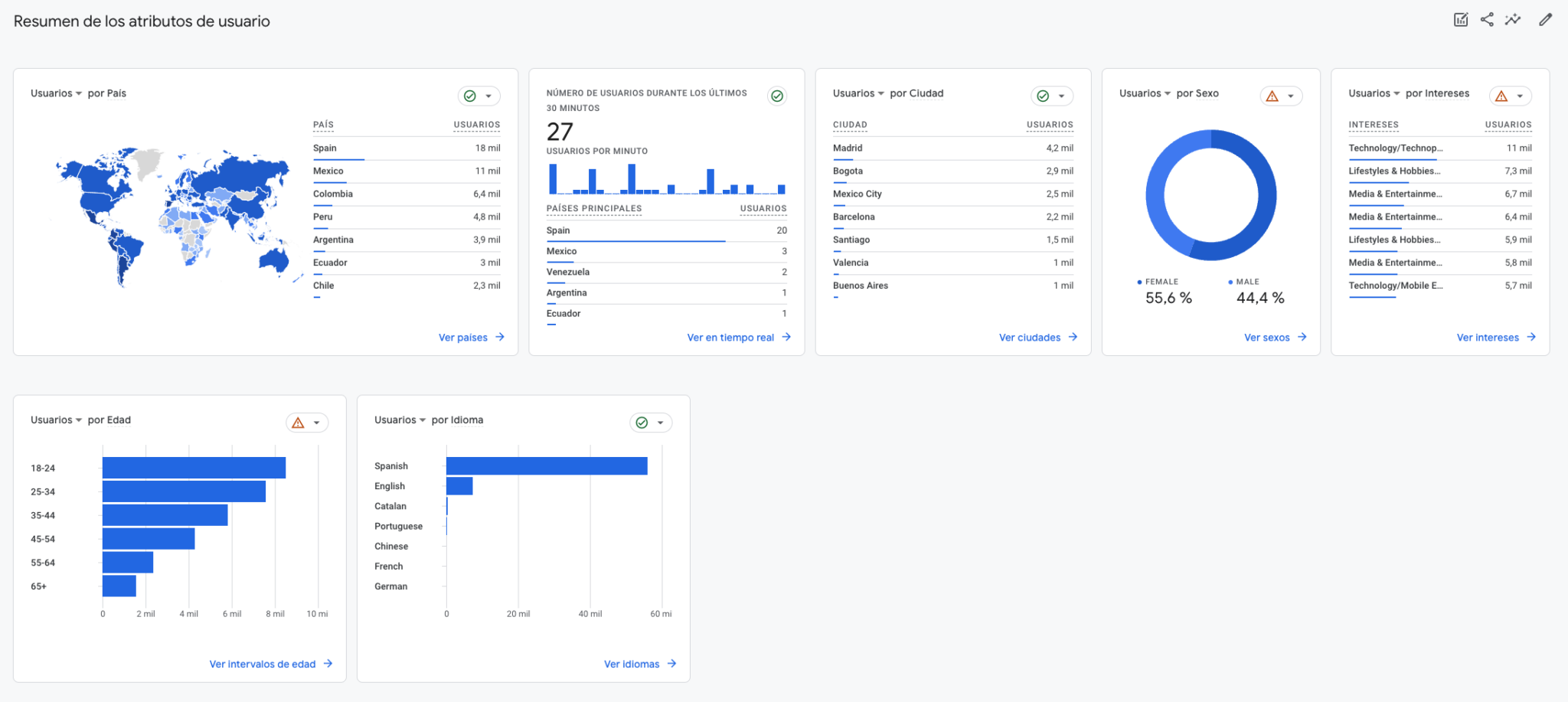
- Study current customers: current consumers of the product or service are a good starting point. Through surveys, interviews or forms on the website we will be able to obtain the data to form this ideal profile. This information can be further granularized from the user interest reports provided by the Google Analytics tool. In addition, in Google Search Console it is possible to check how users who arrive at the company’s pages search, what is most visited… This will give many clues about what content to create and how to focus it.
- Competitor analysis: as long as the competitors chosen for this purpose have a certain track record in the sector, it can be a good idea to analyze their website and determine who they are targeting, with what content and language and what formats they use.
- Sales team: this is usually the part of the company that has the most contact with the consumer, so it can provide key information on customer characteristics.
How to create a buyer persona in 6 steps
To create the buyer persona profile, the company must use the data previously obtained and compose the profile of that ideal customer:
Demographic data
- Gender and age: by attributing an age range and gender it is possible to narrow down the language styles and forms of communication that will get the most engagement from the user. Let us remember that the objective is to maximize the effectiveness of communication actions.
- Geographic location: where the user lives or is located will influence his interests, lifestyle or the current or social topics that interest him most.
- Family situation: this circumstance will largely determine their interests, priorities and consumption possibilities.
- Income: will determine the purchasing level and therefore the possibility of a higher or lower purchase ticket.
- Educational level: the studies the user has completed.
Employment status
In defining the status of the buyer persona in the professional field, it must be taken into account whether it is a professional customer (if we offer a B2B product or service) or if it is an end customer (in case of a B2C business) to adapt our communication to their profile, both in terms of content topics and the type of language used.
The relationship between the company and the user will be closer and longer lasting the more their values and points of view coincide.
It is important that the company has defined which social group its buyer persona belongs to and what opinions it tends to adopt on different social issues. This will allow the company to maintain a communication aligned with these positioning and allow the user to identify more easily with the brand or company.
Defining the user’s life goals is another key point, since it allows us to know what he/she expects to achieve on a personal and/or professional level and to adapt our messages to contribute to this.
4. Pain points
Identifying the buyer persona ‘s pain points is the next step. It is about knowing the problems, concerns or challenges that the ideal customer has.
The information searches you will conduct, or the products or services you will purchase, will be aligned with the objective of solving those pain points.
Therefore, its detection is key to:
- Psychologically align ourselves with our buyer persona and share objectives.
- Define the product and its characteristics: what problem or need it should solve and in what way.
- Plan the company’s communication agenda.
- Generate communication with the right tone and message for the resolution of these challenges. As we mentioned before, one way to determine how the user searches is the Google Search Console tool, which will collect and identify the searches through which users reach the company’s website. In these searches it is possible to detect the presence of specific pain points.
Using as an example a car rental company in a holiday destination, if the company detects that it receives visits through the search “avoid car rental problems” it will be a clue that this is a point of concern for its users. This information will invite you to generate content that attacks and neutralizes that pain point.
5. Motivations and objectives: purchase arguments and competitive advantages.
On the other hand, the company must identify the user’s motivations and objectives. If we know what motivates the buyer persona and what professional or personal objectives he/she intends to achieve, we will be able to generate purchase arguments in line with the objectives pursued by the ideal customer. Converting these objectives into competitive advantages for our product will be a plus.
Returning to the example of the car rental company, you could use customer research combined with surveys to discover that one of their motivations is the flexibility of the service during their vacation and the objective, to explore the place in a comfortable and carefree way.
In this case, the company will be able to compose a buying argument aimed at the buyer persona that focuses on the comfort of the vehicles, their reliability and the peace of mind that this guarantees during the trip.
Competitive advantages include the different price options and characteristics of the range of vehicles or the delivery and pick-up service at the airport.
6. Friction points: counter-objections
The company must take into account the friction points that the buyer persona may encounter during the purchase decision process. Identifying them will allow you to generate content that neutralizes this friction. This will prevent the user from leaving the website in search of such information and abandoning the idea of buying.
Returning to the previous example, the customer who is considering renting a vehicle during his vacation may have various doubts or uncertainties that may hinder the hiring process. Let’s imagine that we determine, during the study of your profile, that one of the main concerns is the quality and maintenance of the vehicles. The reason is that a malfunction of the vehicle, once hired, will surely influence your travel experience.
In such a case, establishing within the same landing page information about the fleet of vehicles, their characteristics and the maintenance process with images that illustrate it would help to smooth this friction point.
As we can see, the company will be establishing a content strategy based on the customer’s expectations, motivations or objections .
With all this we will compose a buyer persona file to be taken into account both when profiling the product or service offered and when carrying out communications through our own media or paid media.
Types and examples of buyer persona
So far we have seen the characteristics and particularities of the main type of buyer persona, the most widespread, which will make up the company’s customer base. This is the so-called decision maker buyer persona, who makes the final purchase decision.
But there are other types of buyer personas depending on their role in the buying decision process. These profiles are characterized by their ability to influence the main buyer persona:
- Prescriber buyer persona: has a direct and active influence on the purchase decision of the main buyer persona, so its role is very close to the moment of conversion. In many cases they are users who have been customers and, from direct experience, recommend the product or service. A satisfied customer who has had a positive experience with the company extremely positive experience is likely to exert a evangelizing or prescriptive role, by leaving positive reviews and comments on the company’s own website, on its social networks or on verified review platforms.
- Influencer buyer persona: profiles that influence, positively or negatively, the decision making process of the main buyer persona. These influencers can be family members, friends or any other person whose opinion is taken into account by the end buyer. Returning to the previous example, let’s imagine a friend of the mainbuyer persona who had a good experience renting one of the vehicles we mentioned. If this friend highlights how easy it was to manage the rental with the company and the good condition of the cars, this opinion will bring the main buyer persona closer to the decision to hire.
- Negative buyer persona: this is the buyer persona profile that is not the company’s target. That is, the profile that has the opposite consumer behavior characteristics to those projected in the ideal buyer persona. Knowing the negative buyer persona has a number of benefits, such as being able to differentiate which profile you do not want to direct the company’s communication to. This will make it possible to save resources, directing content only to the main buyer persona. It will also help us define the message in more detail, so that it fits exactly to the specific characteristics of the main buyer persona.
Returning to the example of the car rental company, if the rental service is more holiday than long-term, a potential negative buyer persona would be users who live year-round in that holiday location. They will probably not aim to rent vehicles on a daily basis or pay these rates, but if they need to rent a vehicle, they will do so through a long-term service, such as leasing. They would be the negative buyer persona of the rental company.
In short: study, define, plan and communicate.
To optimize business communication and adapt it as much as possible to the potential customer, gather data, study and define in detail your buyer persona profile. Plan what content they need to find in relation to your service or product and how they are most likely to consume it.
Take into account their characteristics and generate digital assets (texts, videos, podcasts, publications in social networks…) that meet their need for information and resolution of doubts in the purchase decision process.

