Written by Jose Vicente
Index
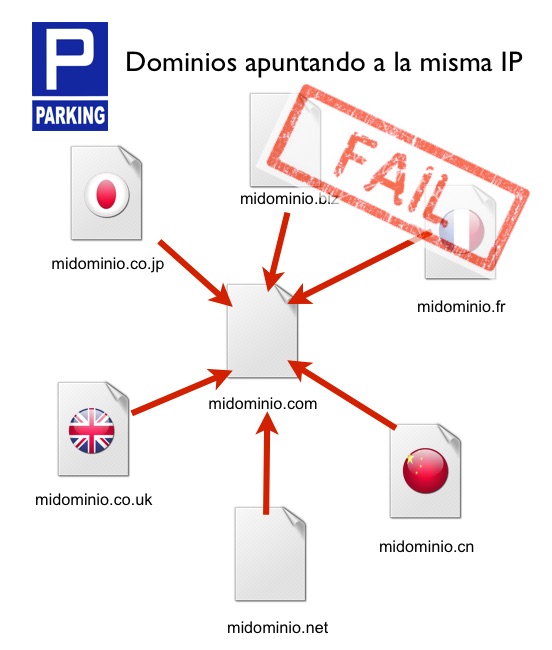
Mirror domains are domains parked on the same IP as the main or canonical domain. When browsing these domains, we access the same content with the only difference being the main domain in the URL. By presenting exactly the same content as this one, they are detected as duplicate content and one of the two will rank well, while the other will be relegated to the supplementary results.
When mirror domains are likely to exist
Frequently, companies buy more than one extension of their domain name in order to protect their brand. They can be gTLD domain extensions – for example, we could buy ourdomain.com, ourdomain.net, ourdomain.biz… – or international ccTLD domain extensions: ourdomain.es, ourdomain.fr, ourdomain.it, etc. You might be tempted to configure all purchased domains to point to the same server (i.e. to the same IP), so that users can visit the website regardless of the domain extension entered.
Although from the users’ point of view this does not pose a problem, from the search engines’ point of view it does, since identical content crawled on different domains will be detected as duplicate content. The most likely result is that only one of the domains will rank correctly.
How we can discover mirror domains
Often, we will discover mirror domains the same way we discover duplicate content: by searching for a literal string of text (remember, look for a sufficiently specific, quoted text snippet in search engines). If a mirror domain exists, search engines will display the result of the mirror domain after the result of the canonical domain (which they consider to be the original and primary source of the content). If we check that all the content matches, then it is most likely a mirror domain.
Problems posed by mirror domains in SEO
One of the problems is that, in this scenario, we cannot anticipate which of the domains will be selected by the search engine as the real origin of the content. It could be the case that search engines index the content on the oldest, most popular or first discovered domain and that this is not the desirable option for the company.
Additionally, and after Google’s Panda update, any scenario in which duplicate content is detected can be potentially dangerous for the positioning of such content regardless of the domain in which it is indexed.
Recommendations to be implemented in mirror domain scenarios
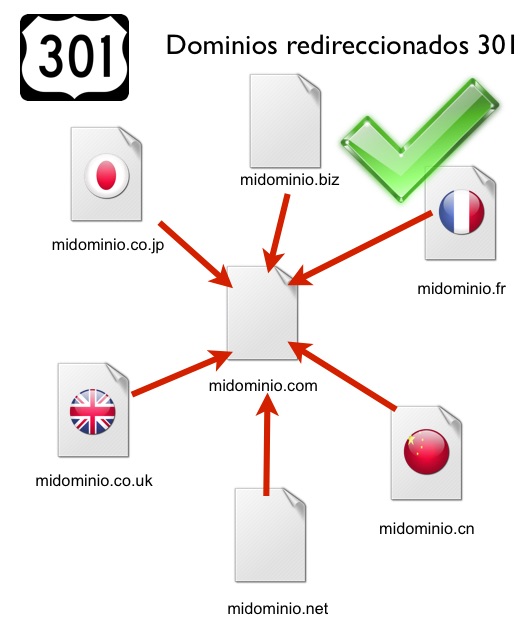
If you own additional domains to your own Web site (for example, with extensions for different countries) and you want any visitor to these domains to be able to visit the pages of your main Web site, it is advisable to program permanent 301 redirections from the secondary domains to the main one. An example of this strategy, fully justified, can be found in the domains of companies such as Häagen-Dazs or Schweppes: it is so difficult to remember the correct spelling of the brand that they bought additional domains with various spelling mistakes. These domains redirect to the main domain with 301 permanent redirects.