Written by Fernando Maciá
Índice
Google presented yesterday at its annual Google I/O developers conference the new features that will soon be available in its various services and products. As it could not be otherwise, almost all of the presentations were related, in one way or another, to the application of Artificial Intelligence and the interaction of Google’s large language models (LLMs) PaLM and PaLM 2 with its own or other partners’ functionalities to offer new capabilities to its users.
The biggest expectation for all of us working in search marketing, however, centered on the impact that artificial intelligence will have on Google as a search tool. So at this point in the presentation I will focus my thoughts on how this new paradigm will affect websites themselves in their relationship with search engines as major distributors of quality organic traffic.
Google SGE features
Cathy Edwards, VP of Engineering at Google, was responsible for showing how the Mountain View search engine is preparing to integrate AI into its search results. These are the main features of how it would affect the way we use Google to find information.
Much more conversational searches
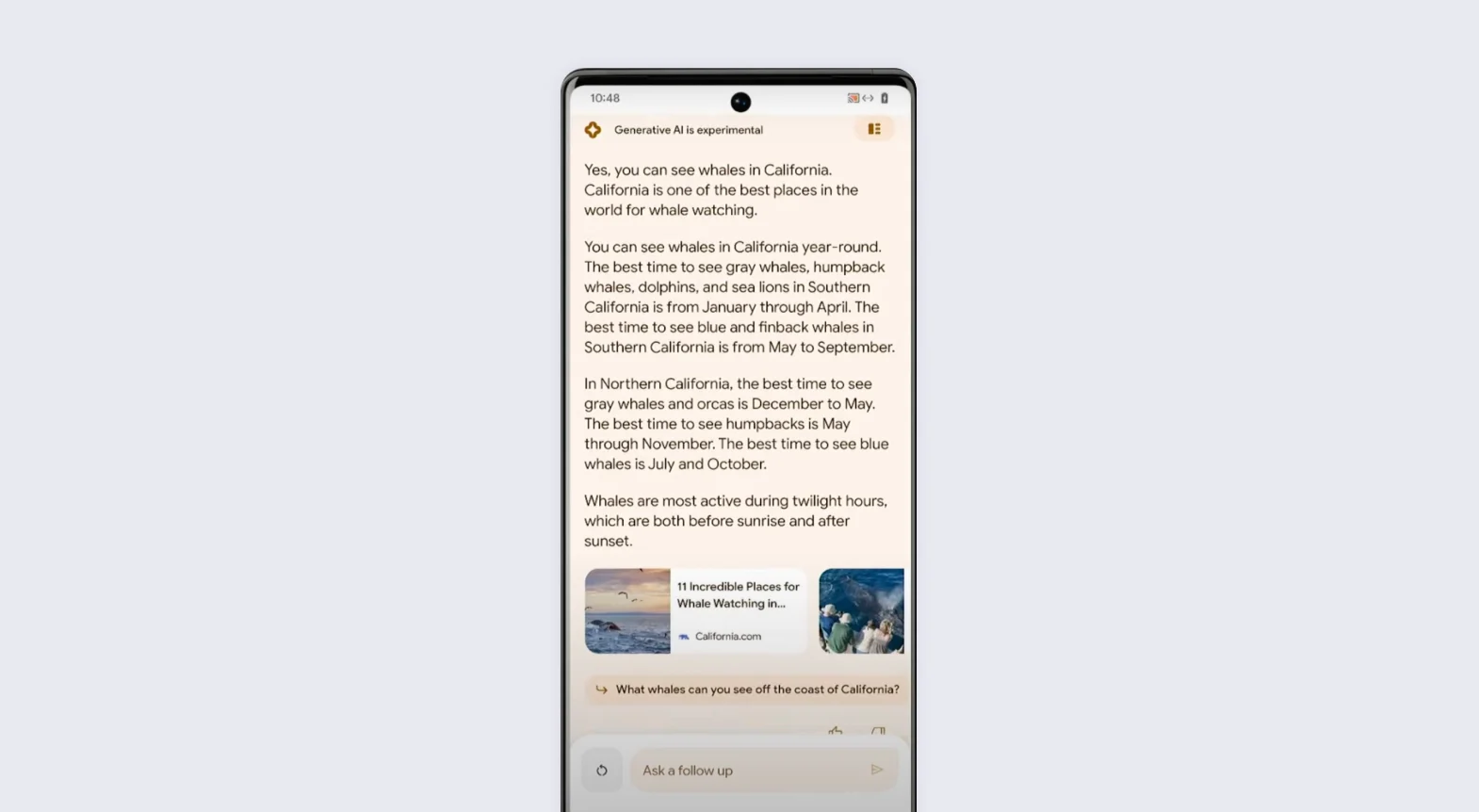
Over time, Google and other search engines have accustomed us to a certain way of formulating our queries in order to obtain the desired results. In general, we usually start the search process with more generic queries and, as we acquire this first information, we consider new, more specific searches to go deeper into certain aspects or resolve additional doubts.
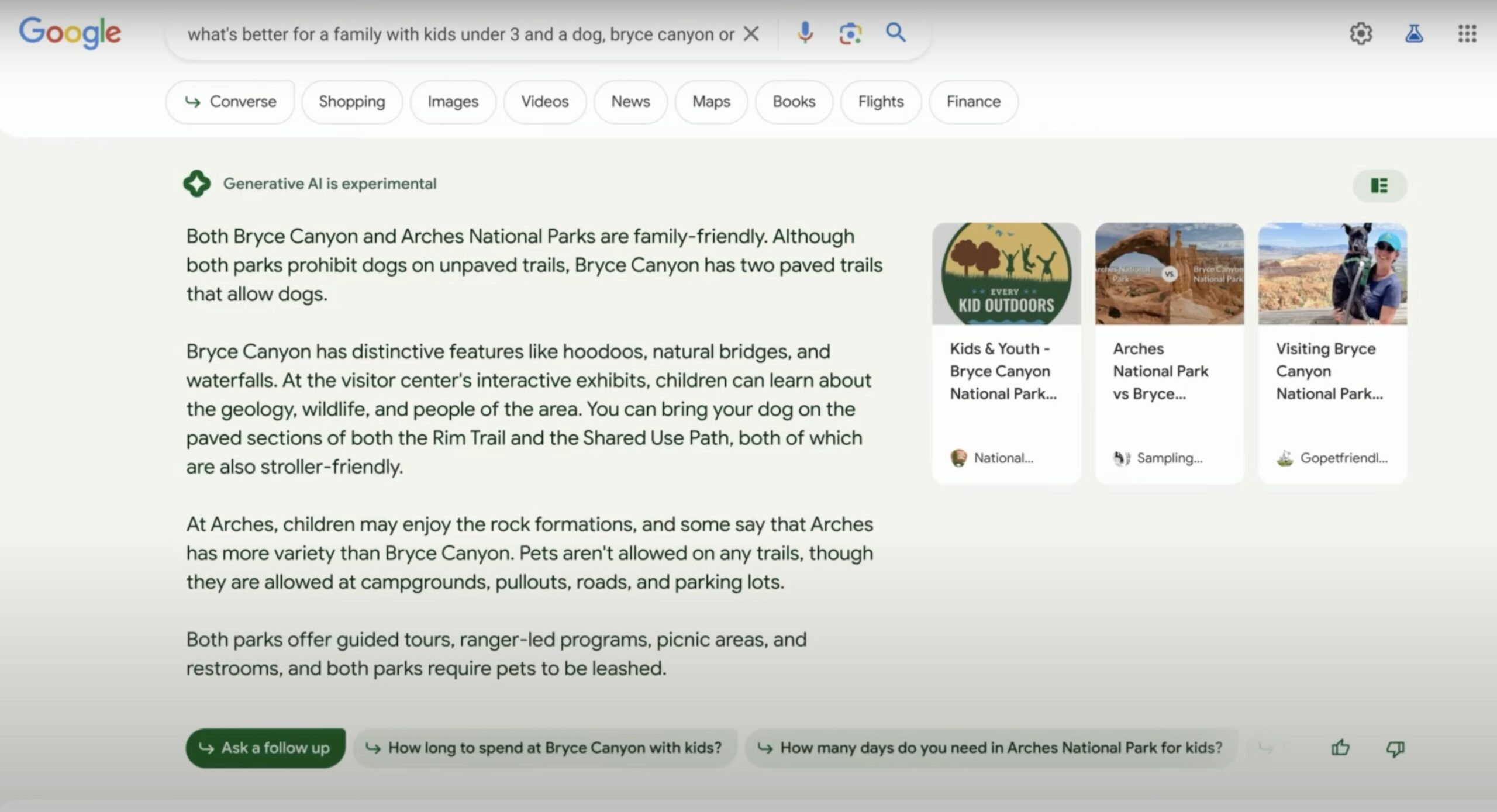
In the example presented by the Google engineer, the query (“Which is better for a family with children under 3 and a dog, Bryce Canyon or Arches”) to find a tourist attraction adapted to these specified conditions is much more like a question we might ask a friend who knows both sites, rather than one we would pose to a search engine.
As we use Google now, we would most likely have used it to find websites with information about both places and would have browsed them to find the information relevant to us: whether they were suitable for children under three and allowed dogs. Once this information was located, we would have chosen our destination.
In the Google example, on the other hand, we delegate this choice to the search engine itself, specifying in the query itself the conditions that the destination must meet, but leaving it up to Google to extract the relevant information and give us a direct response, in the form of a large featured result (“featured snippet”):
The nuance is important, because while the current scenario involves multiple visits to different websites by the user to gather information and make their decision, the new paradigm shifts the entire “customer journey” to the search engine pages themselves, so that the user could complete their choice without visiting any of the websites that Google itself has used as a source of its information.
Contextual grouping of results with links to the original source
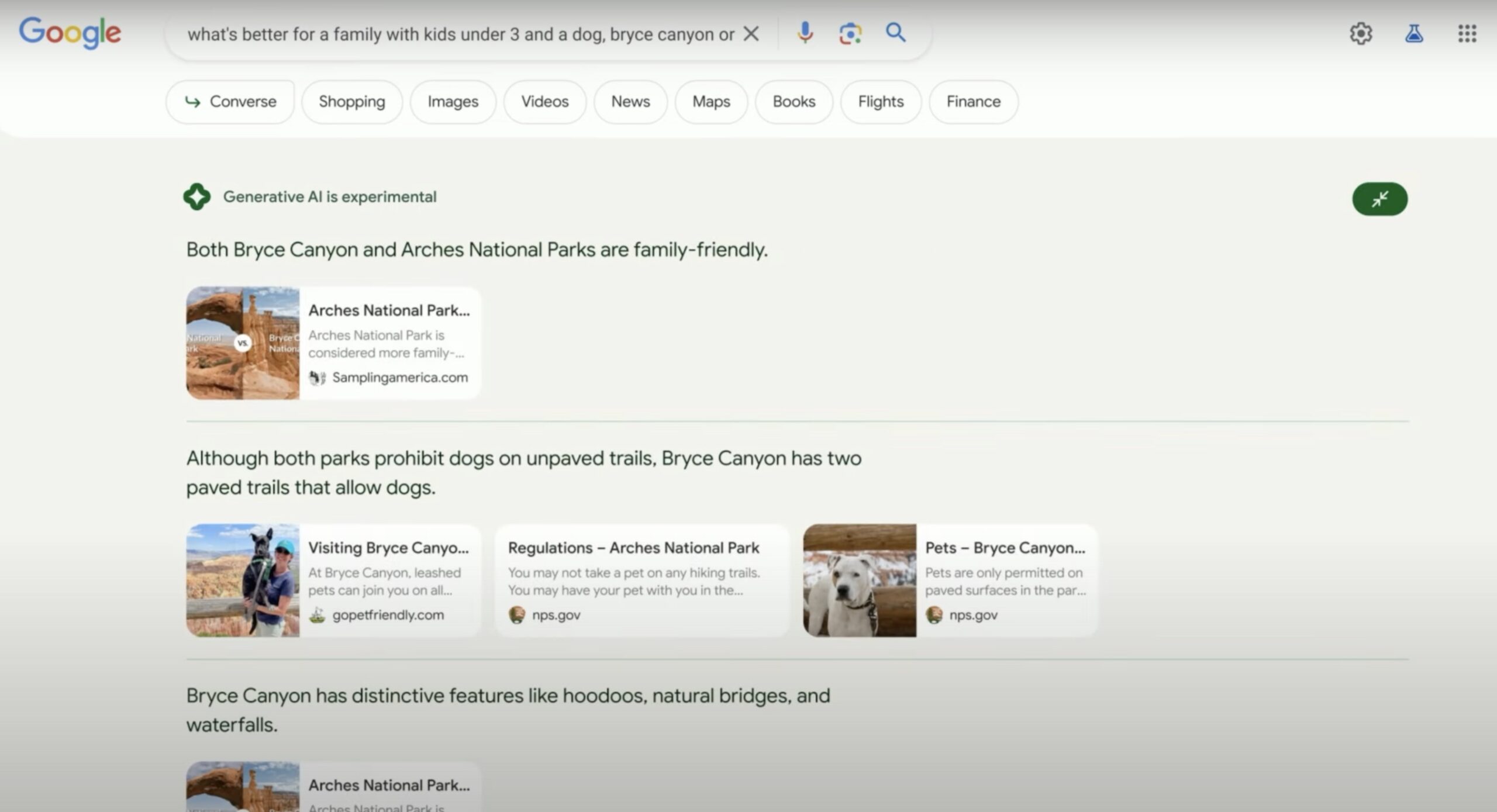
The good news is that, along with the direct result provided by Google, links to websites are maintained where the user can continue to search for more information.
The user can also click on a button that expands the results by grouping them according to the foreseeable search intentions that Google can infer from the context of the original query. In this case, queries related to the possibility of the dog having specific routes for walking, the type of attractions that can be found along the route, etc. where the search engine includes links to different results:
Google calls this view “collaborative” built on top of the sorting and security systems it has been refining for years.
Personal recommendations
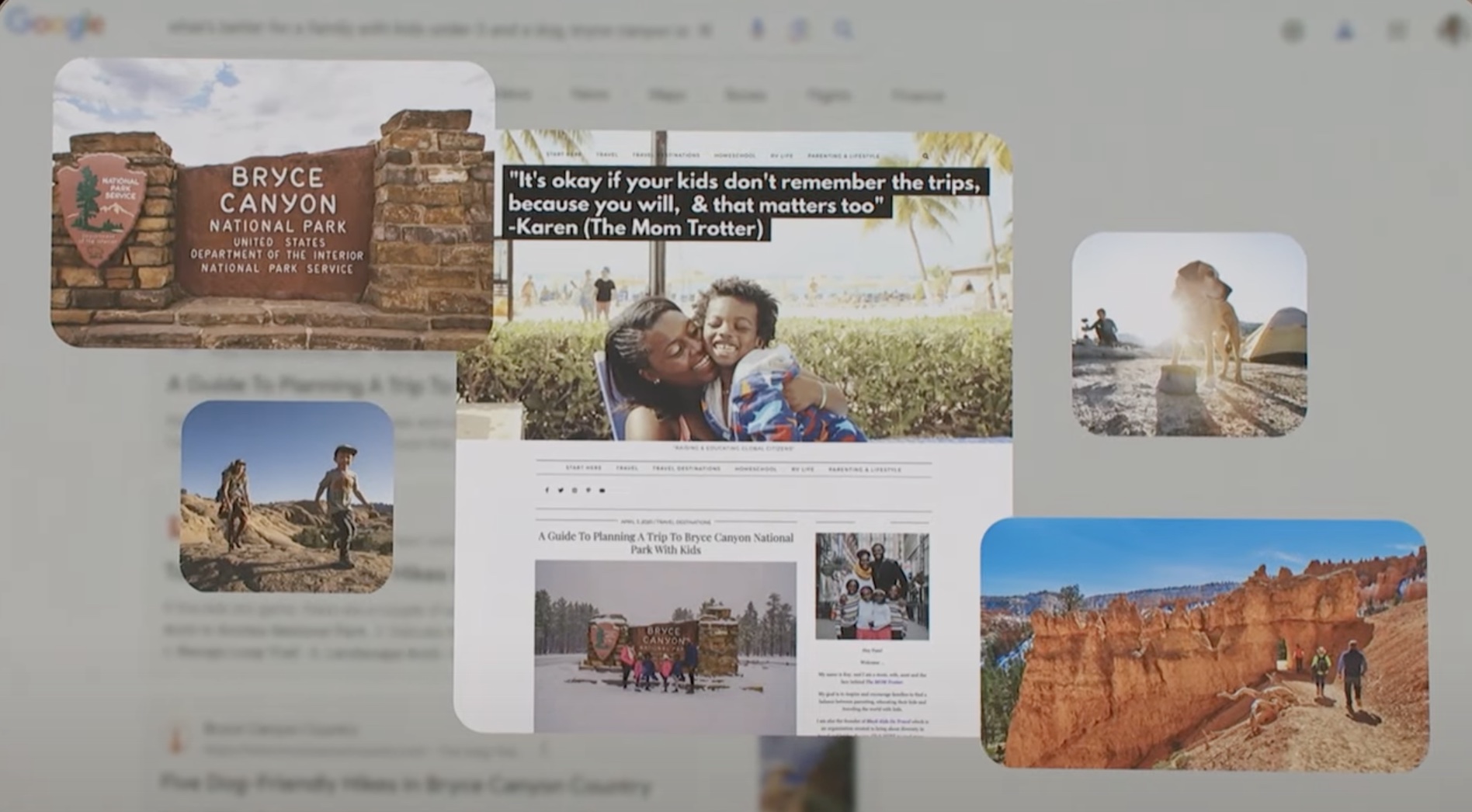
Google also offers the user the possibility to contrast the information with first-hand experience from other users through their Insights, again with links to the original sources of the information:
The key here will be how to build a thematic authority profile to be one of the sources selected by Google for our target search categories.
Obviously, this is bad news for affiliate websites that are not able to demonstrate that first-hand experience with the products or services being analyzed or compared.
Complex searches
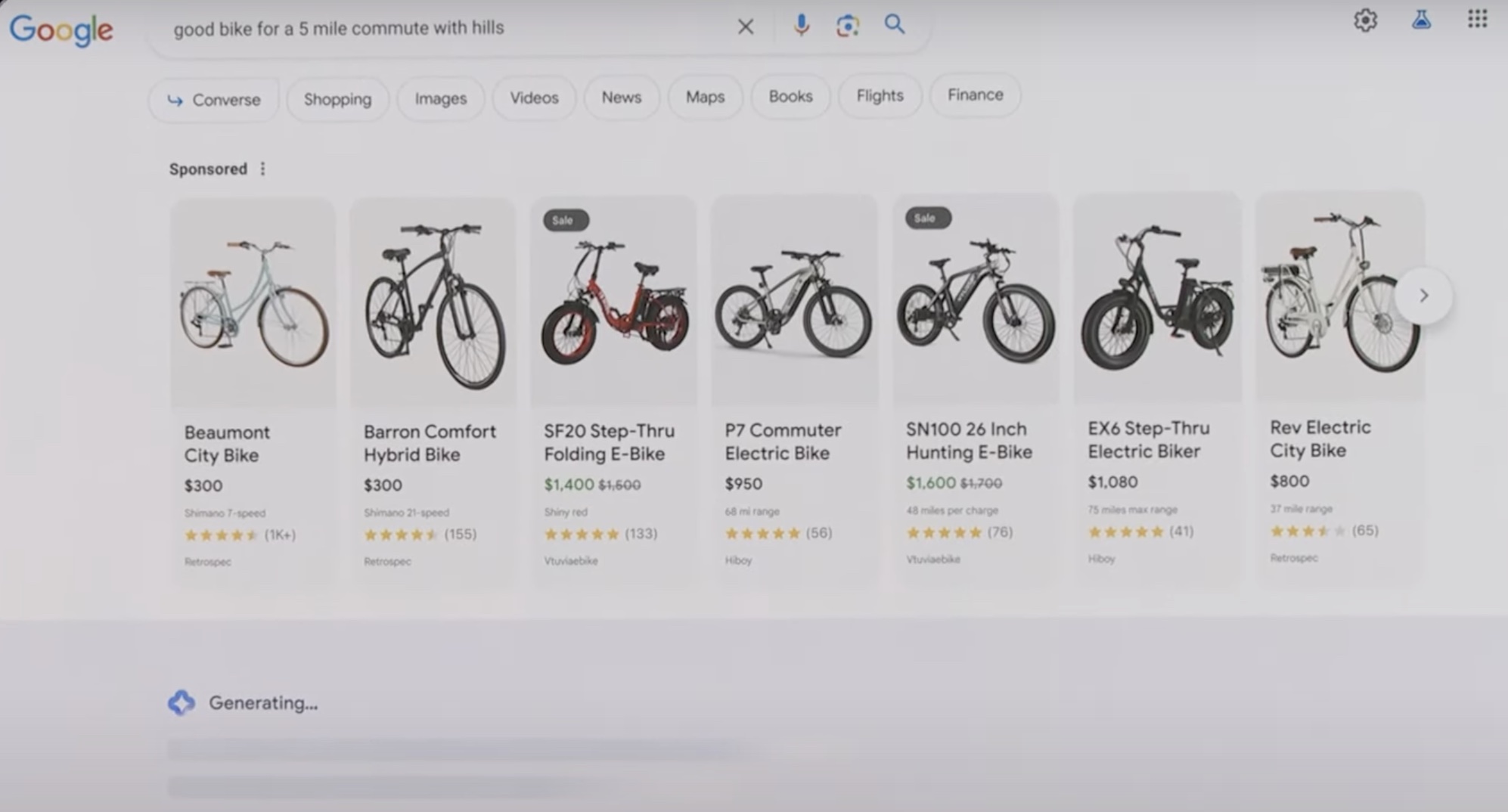
Cathy Edwards also referred to more complex search scenarios where even the user’s questions contain other questions.
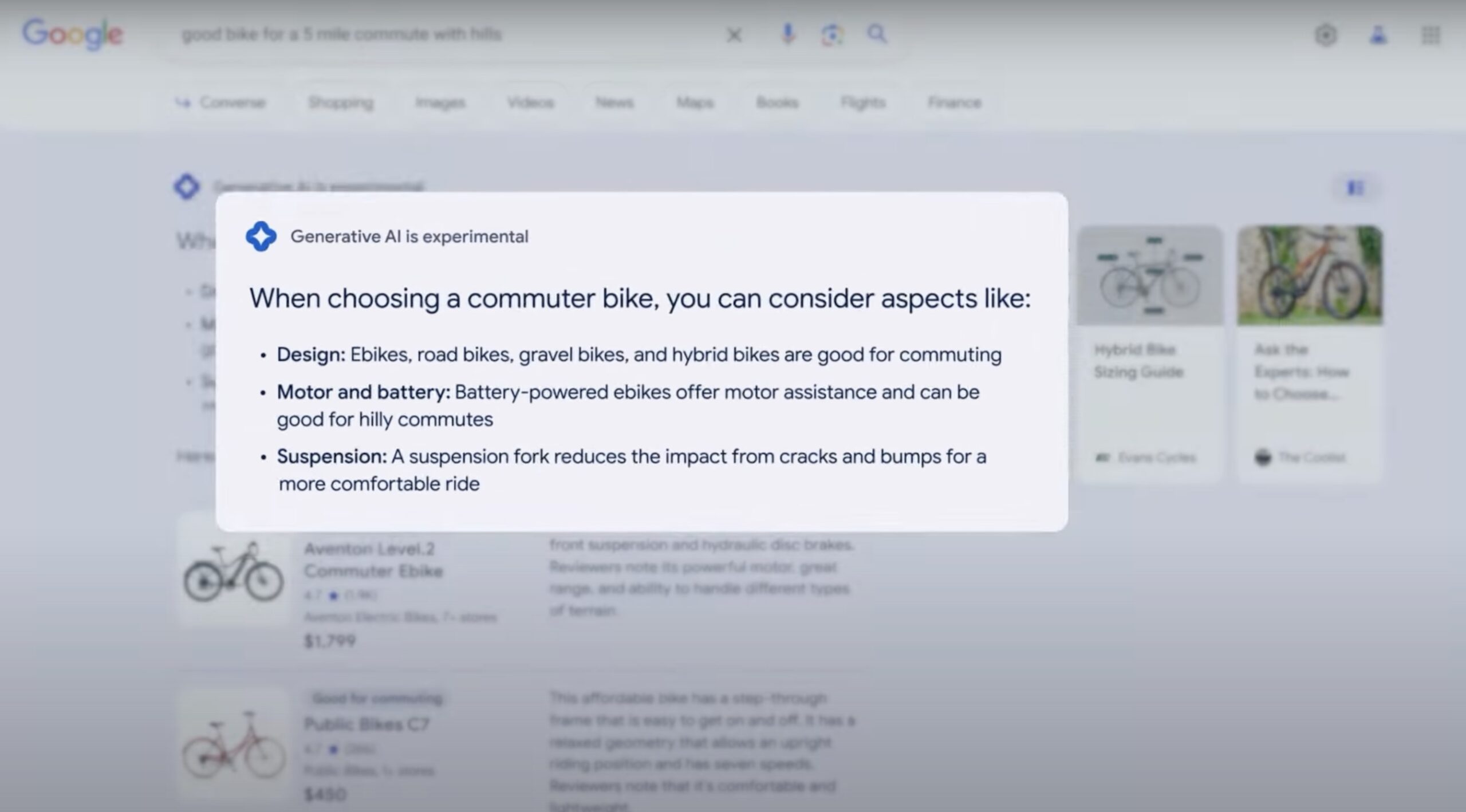
In the example shown (“bike suitable for commuting five miles to work with inclines”), Google displays, as it also does now, a Google Shopping carousel with ads for products relevant to the search:
But in the Generative IA part, it already shows what should be the most relevant features in our choice of product based on the conditions described in the query (design, motor and battery life, suspension…):
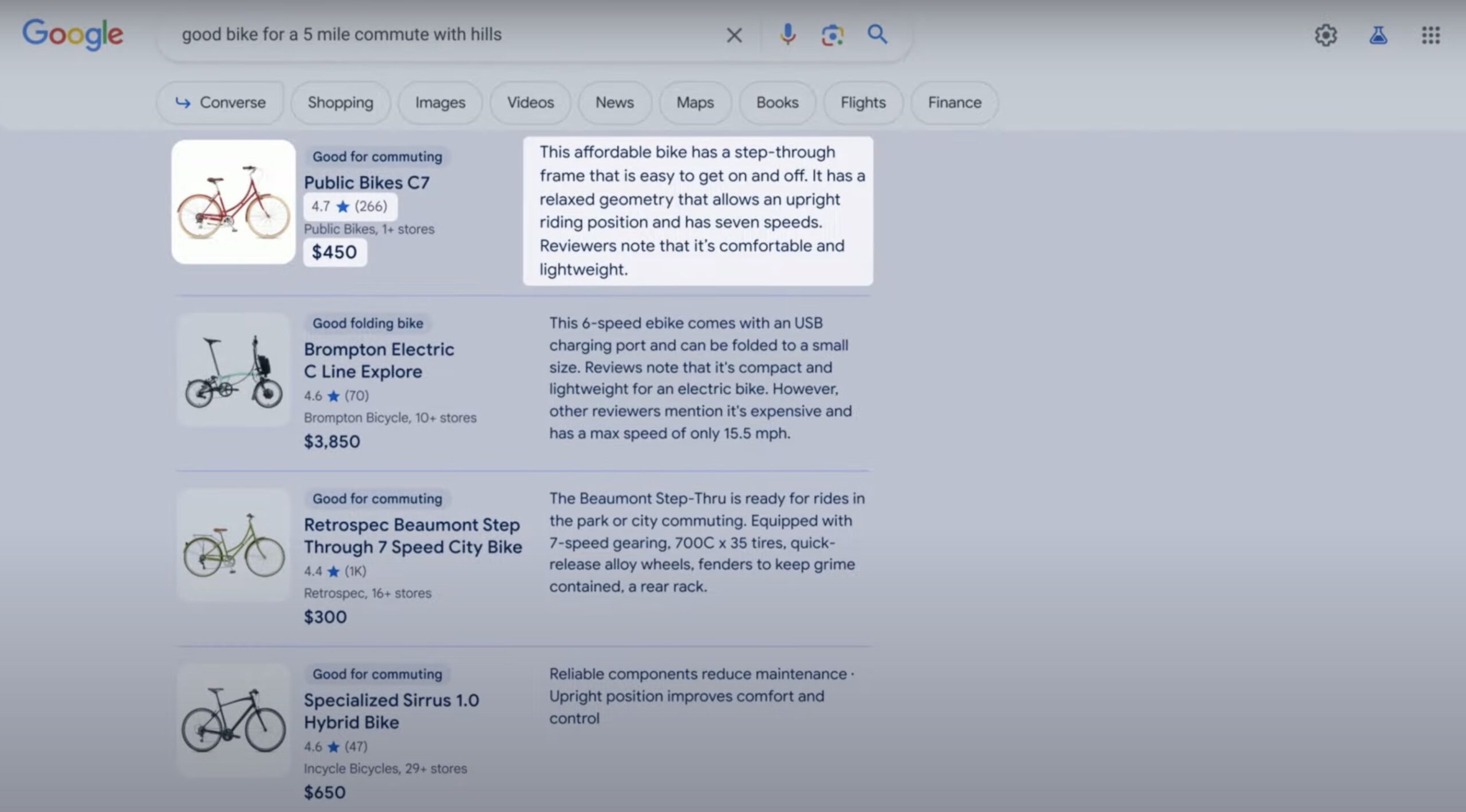
Just below, Google displays products matching the description by highlighting the most contextually relevant features: (“good folding bike”, “good electric bike”, etc.) collecting all features and description from the structured data specified on each website:
All of this is supported by Google Shopping Graph, the world’s most up-to-date and comprehensive product data set including brands, products, reviews, prices and offers from sellers around the world with a portfolio of 35 billion references of which 1.8 billion are updated every hour!
This is a shot at the waterline of marketplaces such as Amazon, Rakuten or Alibaba to regain prominence over users’ product purchasing decisions.
According to Google’s engineer, they are exploring new ways to integrate ads into this product search experience as a way to ensure contact between businesses and their customers.
The user will also be able to move from these results to a new “conversational mode” where they can further refine their search, in the way that filters and facets are applied when browsing an online store, without forgetting the context of the original scenario:
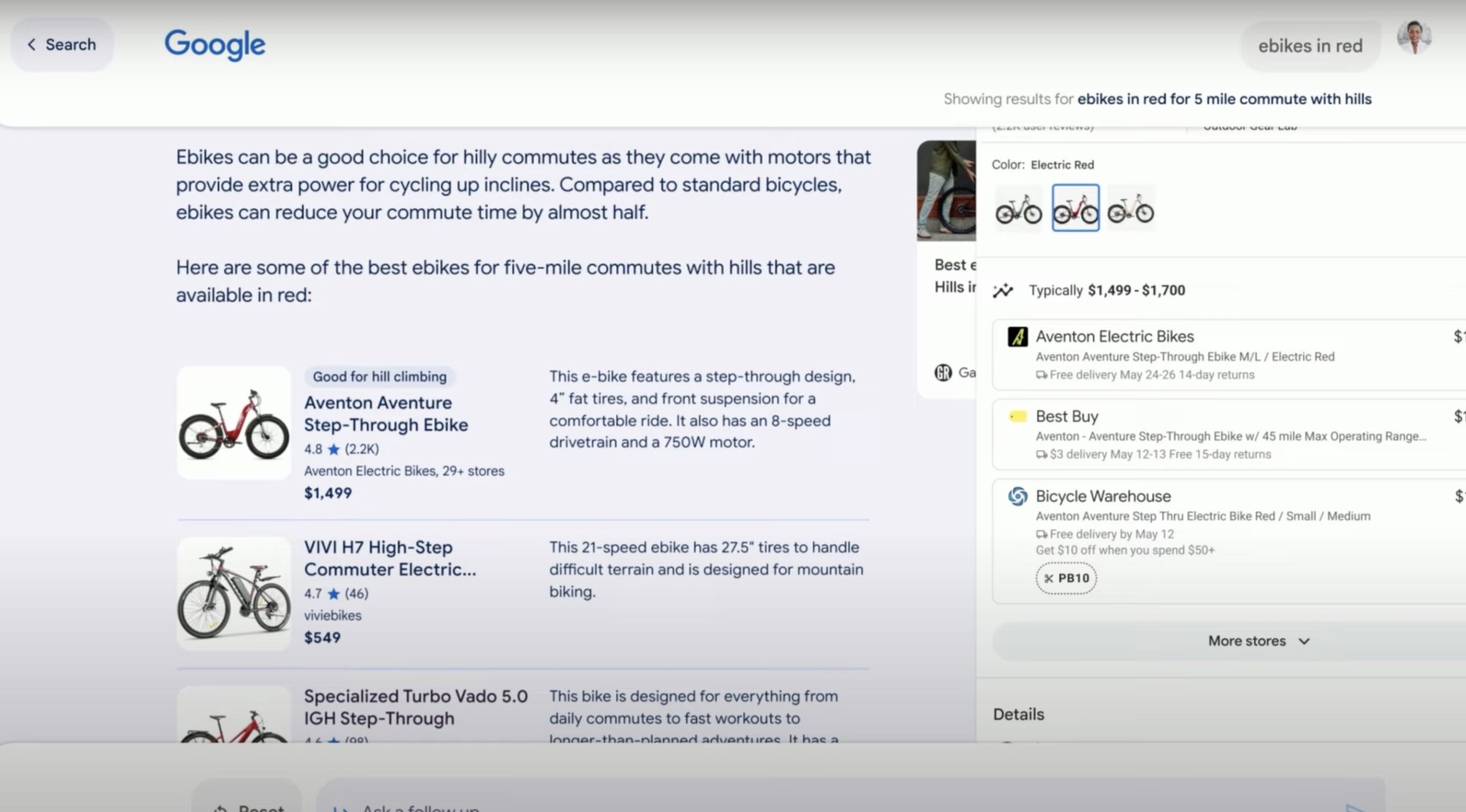
After choosing the product, the search engine will even propose the user to buy from offers from different distributors, just as we are used to seeing them in a traditional marketplace:
The list of results will include the most relevant features according to the context of the search: price, availability, shipping costs, warranty… which relegates the online store to a mere service of dispatching products through your shopping cart.
The user choice process, again, shifts to Google pages. And even if the search process again culminates in a purchase, it forces online stores to ensure full accessibility of their information to the search engine in order to be one of the shopping options included in the results.
And much more
Along with this integration of Generative AI with Google’s search process, we can also use the search engine as an idea and content suggester similar to ChatGPT, for queries such as “give me ideas for a new name for my cycling club”, or “create a social network post about why cycling daily is important”, etc.
In her live demonstration of these functionalities, Cathy Edwards showed how her Generative AI results will be combined with links to related information sources in the form of carousels of snippets under the AI-generated text:
Google allows you to filter the results through successive searches that preserve the context of each of the previous searches, as a filter on the results obtained initially.
For the time being, only in the United States
This new search experience, called Google SGE (Search Generative Experience) will initially be available only in the United States. The URL to sign up for the waiting list is https://labs.google/, but before you run off to run your VPN I will tell you that if your Google account does not have an American PIN check phone, the system will not let you log in either, regardless of your IP.
It is also a requirement to run the application from the latest versions of the Chrome browser or the Google app.
Impact of Google SGE
Effectively, this will change the way we access information and make our decisions as consumers.
It is enormously risky for us to venture how this new paradigm will affect the different online business models. But some of the consequences that we believe may follow from Google’s Generative AI are as follows:
- Google captures a larger portion of the conversion funnel. The user, as in the past, is captured in the early stages of the purchase decision, and accompanied conversationally by suggesting the most relevant features of the products based on their description, ways of filtering the products presented and even with analysis and opinions of users with direct experience of the product. All of these are content formats that in recent years have proven to be extremely effective in attracting user visits, creating loyalty links, establishing a corporate reputation around a specific topic and monetizing a flow of quality organic traffic.
- Now, users could become accustomed to this “tele-directed process” by Google and we could see a much larger drop in visits originating from informational searches that the search engine will now directly resolve. For websites with commercial conversion goals, traffic is likely to suffer more than business results, as the ultimate conversion will still register on our domain. For content websites, on the other hand, this content-predatory behavior on the part of Google could have disastrous consequences.
- Google’s own ranking concept disappears and positions become meaningless. We may talk about a certain sense of “visibility” achieved for certain search categories, but establishing correlations between a given position and related potential traffic becomes irrelevant. The way we measure visibility in the results will no longer be related to position, and this leaves many SEO tools totally offside.
- As SEOs, we will have to find out which are the new rules that help our clients to be among the results suggested by Google SGE. For this purpose, it will be useful to analyze the most relevant product features by usage scenario, implement comprehensive structured data tagging, have first-hand feedback and be able to present a competitive offer that will allow us to stand out in the carousel of purchase options.
- As users, we will see if this new Google proposal is successful or, like so many other previous experiments (Facebook stores and websites with FHTML, Second Life, etc.) it ends up fading away.
- Regulatory authorities will also have a lot to say. The company’s main concerns are: infringement of intellectual property rights over the content used by LLMs for their training, the inclusion of hallucinations among the results returned by the AI that could lead to lawsuits against these companies, or simply problems arising from monopolistic market dominance. On both sides of the Atlantic, warning voices related to these issues have already begun to sound.
- This new scenario forces us to recover the value of brands and the direct conversation between suppliers and users. As specialists in our industry, we will have to be able to work harder than ever to “earn” the loyalty of our customers, remain among their top purchasing choices based on tangible and intangible values they identify with, and offer more targeted and personalized user experiences than a generalist like Google can provide. This is the only way to keep the search engine as an efficient source of new quality traffic, as it has always been, without giving up on establishing and maintaining a close and direct relationship with our customers.
If you want to learn more about this topic, be sure to check out our post on how Google SGE will impact SEO.