Written by Raúl Carrión
Part of the success of an e-commerce is due to the ease with which the customer can make the payment, the simpler it is, the more we will favor the impulse purchase.
We will begin by defining the term online payment:
It is a method that allows the transfer of money between users who wish to purchase a product/service on the Internet.
This method of processing payments can be done through credit cards, savings/current accounts and cash.
These payments are channeled through a platform and each transaction is verified and validated, helping to mitigate fraud as much as possible.
We will now analyze the most common means of payment:
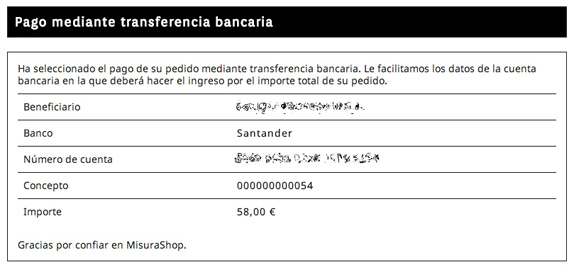
Bank transfer
Wire transfer is a way to move money from one account to another. It is the way to transfer funds between bank accounts without physically withdrawing the money.
When placing an order in an online store by bank transfer, the customer is sent an order code to be included in the transfer order.
Once the merchant detects the deposit in its bank account and verifies that it coincides with a current order, it marks the order as paid and proceeds with the shipment of the merchandise.
It is a method commonly used by users who do not trust entering their credit card information on the website.
Advantages of bank transfer
- Money is received in advance.
- There are no commissions for the seller.
Disadvantages of bank transfer
- The customer may delay payment.
- It may entail commissions for the buyer based on your banking conditions.
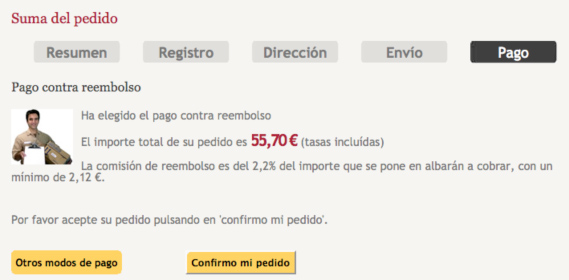
Cash on Delivery
Payment is made upon receipt of the goods. The goods must be checked before payment is made. When selecting this payment method, the online store generates an order code sent to the customer by email along with a summary of the order.
Usually, sending goods C.O.D. involves an additional cost that is billed by the shipping company. It is up to the e-commerce to assume this cost or charge it to the end customer.
Advantages of cash on delivery
- If the customer does not pay for the goods, they are not delivered.
Disadvantages of cash on delivery
- If the customer does not accept the goods, the online retailer shall bear the additional transportation costs.
- It carries commissions (from 2.2% to 5%).
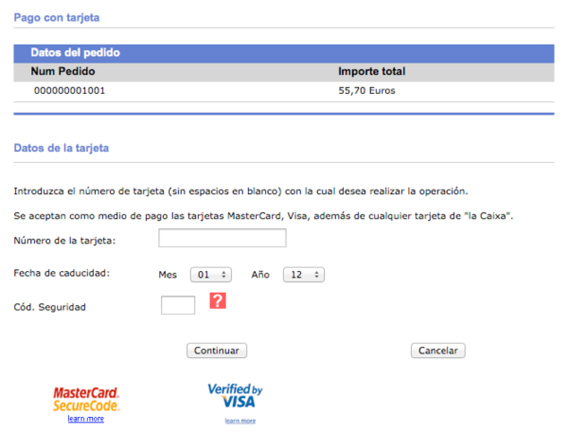
Payment gateway
A payment gateway is an e-commerce service provider that authorizes payments.
It is the equivalent of a POS (Point of Sale Terminal) in a physical store.
The choice of the payment gateway will depend on the bank you work with, your bank will provide you with all the documentation of the gateway used.
It is the most common online payment method.
Advantages of payment gateways
- Money is received in advance.
- It is an immediate payment method.
Disadvantages of payment gateways
- It carries commissions for the seller.
Operation of a payment gateway
A payment gateway works in stages, below we detail the actions performed in each one of them:
- The customer generates an order.
- The online store sends the order data to the gateway.
- The payment gateway requests the card information from the buyer.
- The payment gateway sends the information to the credit card issuer.
- The credit card issuer informs the payment gateway of the acceptance or rejection of the transaction.
- The payment gateway returns to the online store the status of the transaction.
- The store informs the customer of the acceptance or rejection of the purchase.
PayPal

The behavior of PayPal varies from country to country, but in general it offers these modalities.
- Work with money previously deposited in the PayPal account.
- Work as a bank payment gateway, requesting credit card data.
Advantages of PayPal
- It is secure, the customer’s financial data is not shared with the seller.
- It’s fast, all you need to buy is your PayPal login details.
- Flexible, you can fund PayPal by debit card, credit card, wire transfer or from another PayPal account, or you can use it as a payment gateway.
PayPal Disadvantages
- It carries commissions for the salesperson based on sales volume.
- It entails commissions for the buyer when there is a currency exchange.
Installing PayPal
To offer PayPal payments for your e-commerce, the first step is to sign up for a PayPal business account.
PayPal offers three service variants:
- Standard payment: no monthly fee, so you only pay for what you sell.
- Comprehensive gateway: it has a monthly fee of 15€ plus a variable and offers more functionalities than the standard version, such as the possibility to customize the design to integrate it perfectly into the website or the sales protection to minimize frauds.
- Express payment: ideal complement if you already have a credit card gateway. It consists of a button that allows you to pay with PayPal in just three clicks.
Once the service is contracted, you will need to install a PayPal management module or program it from scratch, if it is a custom development, which will allow you to connect to the PayPal service with your username and password.
Sagepay

You will have to calculate from your business billing data how the amount of the fee is distributed among all the monthly transactions to evaluate if it is more economical than the alternatives previously mentioned.
The Sagepay gateway performs two actions:
Payment processing
The steps Sagepay takes when a customer purchases a product are as follows:
- Once the customer completes the order, Sage Pay securely captures the credit card information.
- If the customer is registered with the 3D Secure security processes, they will be prompted to enter their Verified by Visa or MasterCard SecureCode password on their card issuer’s page (optional).
- The merchant bank will send the credit card details to the customer’s card issuer, who will authorize or decline the transaction.
- The merchant bank will then return the transaction results to Sage Pay.
- Sage Pay sends you the results of the authorization and also sends them to the customer to confirm the outcome of the transaction.
Settlement of payments
Each day Sagepay will settle payments with the e-commerce as follows:
- At the end of the day, funds from all processed transactions are sent to the merchant bank for settlement.
- The merchant bank then collects the funds from the card issuer and credits your bank account. The deposit of funds into your account varies from bank to bank.
Other forms of payment
Money order
The traditional money order service offered by the post office. The buyer pays for the service and the seller ships the goods upon receipt.
Western Union
The buyer delivers the money to a Western Union agency, which notifies the agencies in the seller’s city to pick up the shipment.
When the transfer is made, the buyer receives a key that must be sent to the beneficiary seller so that he can withdraw the money.
Direct debit
The seller collects directly from the buyer’s bank, who has given prior authorization.
Prepaid chip cards
The card is reloaded with money at the ATM and the money it contains is available for spending at any time.
This “cash” system is particularly suitable for small purchases, the so-called micropayments.
I recommend…
Once all these payment methods have been analyzed, my recommendation is to have at least a bank transfer and a bank gateway. And if possible PayPal.